They help start-ups – but who exactly are business angels?
In a recent study, Prof. Dr. Richard Geibel, Dean of Studies at the Fresenius University of Applied Sciences, together with Zhiyao Feng from the MIT Center for Real Estate, Cambridge, and Robin Kracht from the E-Commerce Institute of the Fresenius University of Applied Sciences, has dealt with the characterization of business angels and their influence on the success of start-up companies.
The study “Characterizing Business Angels” examined business angels of nine successful companies [1] for similarities. A total of 2,144 business angels (BAs) were examined in detail. So far, BA’s have not received much attention in this country, especially in comparison to venture capitalists (VC), although they can be assigned equal importance. In doing so, they not only pass on financial resources, but also experience and contacts.
CHINA AND THE BUSINESS ANGELS
According to Statista [2] and “The Wall Street Journal” [3], four of the ten highest rated start-up companies worldwide came from China in 2018. Angel investments are far more common in China than here.
In China, BAs have already been divided into five categories [4]:
New asset groups with foreign degrees or top management positions in foreign companies
People with high income
Rich heirs
Foreigners or experts with strong interest in the Chinese market
Investors supported by the government
WHO OR WHAT ARE BUSINESS ANGELS?
Business Angels are wealthy people, mostly former entrepreneurs themselves, who invest their money in the early development phases of a company.
BAs often start their careers in both technical and business management areas. They gain experience and capital over years until they start their own business in their industry. Then they change from entrepreneurs to BA and invest in start-ups. In addition to the capital, they bring experience, know-how and contacts to the table. They are rarely active in the operative business.
If this investment is successful, they support further start-ups. This ecosystem creates a win-win situation for BA’s and start-ups. BAs are often organized in networks.
Business angels and their investments are usually active during the start-up or shortly thereafter, i.e. in a phase that is associated with a high level of dynamism in the young company. Although start-ups have a large share of innovative power in various industries, they still face major problems in the start-up financing of their company.
COMMON FEATURES OF THE BUSINESS ANGELS
The evaluation of the “Characterizing Business Angels” study clearly showed that some characteristics of the BAs are recurring in companies in which investments were made and which were then successful.
Since the BAs are not only financiers but also mentors, the characteristics have an influence on the success of the company.
These common characteristics include academic education, experience as an entrepreneur and professional experience in various management positions.
CASE STUDIES
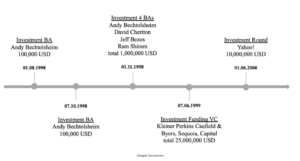
When Google was founded in 1997, founders Larry Page and Sergey Brin didn’t believe in the immense success their company would one day have. But the first three investors were BAs, and these first five rounds of financing brought in as much as $36.2 million.
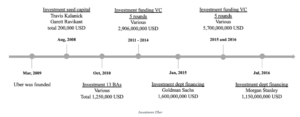
The US service company Uber, which offers passenger transport mediation services via apps in many cities around the world, also bases its business success on the investments of a few BAs.
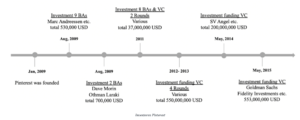
Pinterest, founded in 2009, was initially strongly supported by BAs. The first four rounds of financing in this company were exclusively provided by BAs.
Although Pinterest now has over 300 million monthly active users worldwide[5], it took some time before this app was accepted by users. Initially, there were 19 BAs out of 21 investors, including Marc Andreessen, co-founder of Netscape Communication.
BUSINESS ANGELS IN THE GERMAN MARKET
Currently Robin Kracht is working on an extension of this study for the German market. The aim is to find out which are the same and which are different characteristics of the BAs in different countries. Furthermore he wants to create deeper insights into the importance of BAs and VC in order to identify the success factors and to define standards.
Article available at: https://www.adhibeo.de/sie-helfen-start-ups-doch-wer-sind-business-angels-eigentlich/
Sources:
[1] Google, Uber, Grockit, Pinterest, Affirm, Fourscare, Alibaba, ofo and DayDayUp
[2] https://www.statista.com/statistics/407888/ranking-of-highest-valued-startup-companies-worldwide/
[3] https://www.wsj.com/graphics/billion-dollar-club/
[4] Liu, M., and Chen, B. (2007). Business Angel Investment in the China Market. Singapore Management Review, 2007 2 [5] https://business.pinterest.com/en