Digital Customer Engagement – The “diCE Model
E-Commerce Institute (HS Fresenius) and ORT Medienverbund cooperate.
Corona is causing typical sales patterns to change, and companies are losing their personal proximity to their customers. Replacing traditional sales activities with new digital concepts alone is not enough. ORT (Agency Group for Sales and Marketing) and the E-Commerce Institute of the Fresenius University of Applied Sciences have set themselves the task of developing a new and scientifically tested sales model that achieves customer proximity through lasting, relevant and integrated customer engagement along the customer journey in order to ensure maximum sales success in the future.
On this page you can now follow the progress and results of the cooperation.
The diCE-Modell:
Successful sales in times of Corona and beyond
Problem definition and derivation
“(…) COVID-19 has pushed companies over the technology tipping point-and transformed business forever” (McKinsey Company 2020a, n.p.).
Many things are no longer the way they were before COVID-19. Customer events or trade shows no longer take place, restaurant visits are prohibited, personal contacts are limited, schools are closed, offices are empty. Many people fell ill, and the health care system is reaching its capacity limits. The COVID-19 pandemic forced the entire population to change (Zeuge, Weigel, Niehaves, Oschinsky & Schlechtinger 2020). In addition, the pandemic significantly increased and accelerated the use and adoption of digital technologies. The entire global population was confronted with an unpredictable situation and had to immediately adapt their daily lives. This also had a significant impact on the world of work and transformed the way companies in all industries and regions do business (McKinsey & Company 2020a). Many digital projects were initiated, launched and implemented. Digital adoption among consumers and businesses jumped forward five years in about two months (McKinsey & Company 2020b).
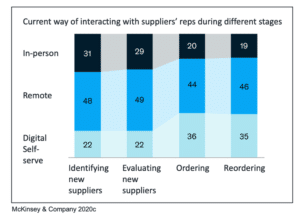
In the area of sales, too, the COVID 19 pandemic necessitated an enormous digital transformation among B2B buyers and B2B sellers (McKinsey & Company 2020c). During the lockdown, field sales visits or face-to-face meetings with customers were almost impossible and very limited (Kober 2020), i.e., companies lose the personal proximity to their customers. But what initially started as a crisis response has now become the new normal, with significant implications for how buyers and sellers do business in the future (McKinsey & Company 2020c). “For B2B sales, digital is the wave of the future” (McKinsey & Company 2020c, n.p.).
This is because the topic of accelerated digital transformation is becoming increasingly important in this industry, and in the future, sales success will depend even more than before on successful digitization (Kober 2020). During COVID-19, new opportunities emerged for the use of virtual tools in B2B sales, which enabled companies to maintain their business continuity. More and more interactions with customers or partners are now virtual. This rapid, industry-wide shift to “digital-first” has thus led to a significant increase in the technology affinity of B2B sales teams. For many companies, the global pandemic has disrupted previous sales operations. But thanks to new technologies, many companies are recovering from the crisis and finding their way back (Accenture 2020). A recent study by McKinsey & Company shows that since last year, face-to-face interactions in traditional B2B sales have declined by 52%. In contrast, there has been a significant increase in digital interactions. Digital offerings such as video conferencing have increased by 41% and online chats by 23% (McKinsey & Company 2020c).
But it’s not just workflows that have changed, it’s also the mindset of employees. Most B2B activities have shifted to virtual and digital. And even in sales, this mindset will not completely regress after the COVID-19 pandemic, but will affect the business in the long term (McKinsey & Company 2020c). “More than three-quarters of buyers and sellers say they now prefer digital self-services and contact with remote employees to face-to-face interactions” (McKinsey & Company 2020c, p. 2). Rather than feeling compelled to digitize in response to widespread shutdowns in the early stages of COVID-19, B2B sales managers are increasingly convinced that their business is going digital. Only about 20% of B2B buyers hope that processes will return to pre-pandemic “face-to-face,” even in industries where traditional field service models have dominated. Especially in the area of ordering and reordering, interaction is shifting toward digital communication (McKinsey & Company 2020c).
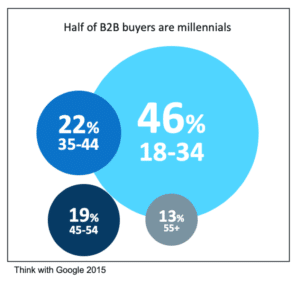
But it’s not just the global pandemic that is accelerating digital transformation; the generational shift in B2B buyers is also having a significant impact. A study by Google and Millward Brown Digital showed that almost half of B2B buyers today are Millennials (Think with Google 2015).
This generation is digital, online-savvy and mobile. They are active on social platforms such as LinkedIn and YouTube, where they absorb information online. There, in addition to white papers or glossy brochures, they primarily consume videos. They also expect quick answers and a high availability of services and information. Personal contact is therefore less in demand. The focus is on a fast and uncomplicated handling of the purchasing process (Think with Google 2015). This change leads to new decision chains. For this generation, the Internet has long since established itself as a research source in the area of sales. It is usually the first touchpoint in the customer journey. For this reason, it is becoming increasingly important to provide the information required by the buying center in real time and without hurdles (Hahn 2020).
Government-mandated safeguards and social distancing regulations around the world have forced companies to move field operations in-house for the foreseeable future. However, many of these processes will continue to be retained voluntarily in the future. This shift raises many questions: What’s next? How can sales survive and even thrive in these new and dramatically changed times? How can companies increase the effectiveness of their virtual sales teams?
The current changes confront sales not only with new customer requirements and diverse opportunities and challenges of digital transformation, but also with diverse new opportunities to support and accelerate sales through digital modules. The moment for reinventing business models and integrating the value creation of companies into a new social landscape has thus now arrived.
The solution is therefore to completely redefine the sales journey. In this process, new moments of truth are uncovered and sales approaches are changed to provide an increase in convenience and transparency in all customer interactions (Accenture 2020).
Against this background, the E-Commerce Institute of the Fresenius University of Applied Sciences, together with the agency group for sales and marketing ORT, is developing a new type of integrated approach to provide a suitable solution for companies in the face of radically changed framework conditions. This solution approach includes comprehensive digital support for all customer touchpoints within the framework of the customer journey and is referred to as the “diCE Model: Digital Customer Engagement Model“. Essentially, the previous tried-and-tested forms of face-to-face communication within the framework of customer interaction are supplemented and expanded by appropriately integrated, digital modules and support approaches. In this way, a permanently relevant customer engagement is achieved that will also allow the greatest possible sales success in the future.
References
Accenture, 2020 The New World of B2B Sales – React, Adapt, Rise, viewed 18 March 2021, from https://www.accenture.com/_acnmedia/PDF-126/Accenture-The-New-World-of-B2B-Sales-1.pdf.
Hahn, T., 2020, ‘Kunden verstehen – Impulse setzen’, eCOM MAG E-Commerce und digitaler Wandel, No. 4, 2020, p. 23.
McKinsey & Company, 2020a, How COVID-19 has pushed companies over the technology tipping point—and transformed business forever, viewed 29 February 2021, from https://www.mckinsey.com/business-functions/strategy-and-corporate-finance/our-insights/how-covid-19-has-pushed-companies-over-the-technology-tipping-point-and-transformed-business-forever.
McKinsey & Company, 2020b, The COVID-19 recovery will be digital: A plan for the first 90 days, viewed 06 March, 2020 from https://www.mckinsey.com/business-functions/mckinsey-digital/our-insights/the-covid-19-recovery-will-be-digital-a-plan-for-the-first-90-days.
McKinsey & Company, 2020c, These eight charts show how COVID-19 has changed B2B sales forever – New analysis makes it clear: For B2B sales, digital is the wave of the future, viewed 06 March 2020, from https://www.mckinsey.com/%7E/media/McKinsey/Business%20Functions/Marketing%20and%20Sales/Our%20Insights/These%20eight%20charts%20show%20how%20COVID%2019%20has%20changed%20B2B%20sales%20forever/These-eight-charts-show-how-COVID-19-has-changed-B2B-sales-forever.pdf?shouldIndex=false%20%20%20%20%20%20Why?
Think with Google, 2015, The Changing Face of B2B Marketing, viewed 14 March 2021, from https://www.thinkwithgoogle.com/consumer-insights/consumer-trends/the-changing-face-b2b-marketing/.
Zeuge, A., Weigel, A., Niehaves, B., Oschinsky, F. & Schlechtinger, M., 2020, Leading Virtual Teams – A Literature Review, viewed 25 February 2021, from https://www.researchgate.net/publication/343473371_Leading_Virtual_Teams_-A_Literature_Review.
Authors: Antonia Biel and Simone Schreiner of the E-Commerce Institute.
Other people involved:
Prof. Dr. Richard C. Geibel (Dean of the Master’s program in Digital Management at Fresenius University of Applied Sciences).
Robin Kracht (Head of Digital Transformation at ECI, lecturer in online marketing and doctoral student).
We will continue with the next update soon!