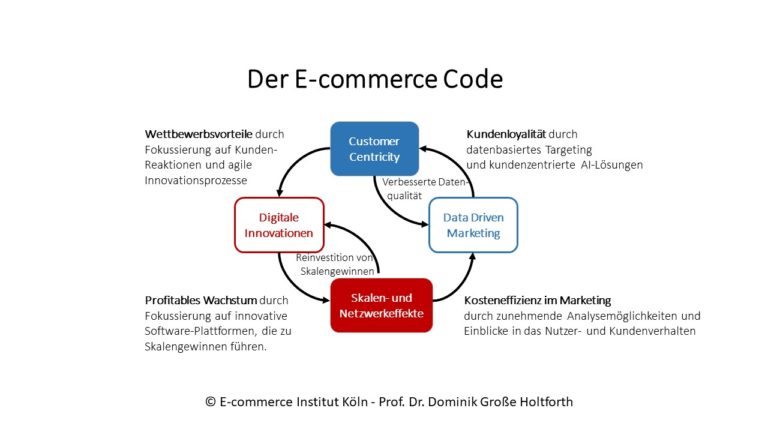
The e-commerce code – the most important e-commerce success factors
E-commerce success factors are motors for growth and profitability for every e-commerce company. Used correctly, they can set a flywheel in motion for greater success in e-commerce. With the e-commerce code, the E-Commerce Institute has placed four central success factors at the center of its work, which contribute significantly to the expansion of the leadership role of the world’s leading e-commerce companies.
This video gives an overview of the e-commerce code:
The starting point of the analysis is the behavior of e-commerce market leaders such as Amazon or Zalando. Their strategies lead to a control loop model for e-commerce. In this, four central strategic success factors are decisive for the development of long-term competitive advantages. These four success factors are
- Customer Centricity
- Digital innovations
- Economies of scale
- Data-Driven Marketing
First, the factors are placed in a strategic context.
E-Commerce Success Factors – The Model “The E-Commerce Code”
Digitalization has already significantly changed the marketing and sales of goods and services. The two central drivers for this development are technological innovations on the one hand and a high level of acceptance for these innovations among consumers.
In particular, the functions of information, communication and transaction, i.e. the sale of goods, have so far expanded considerably as a result of digitalization. It can be expected that in the subsequent phases of digitalization, production – through networked machines and the digitization of factories – will also be subject to massive change. Ultimately, it can be predicted that in the future, innovation and creation will also be changed by digitalization, in which artificial intelligence and continuously growing computing power can be used.
This transformation of important social and economic functional areas is the basis for successful e-commerce strategies and e-commerce success factors. Companies that adapt to change the furthest and most successfully use the potential that opens up have the greatest competitive advantages.
The model “The E-Commerce Code” puts four strategic success factors in context and thus helps to better control e-commerce business models.
The success factors and their role in the model are presented below. Then the requirements and examples for the application of the success factors in digitalizing companies are given.
Success factor: Customer centricity
The starting point of the model is the “Customer Centricity” factor. “Customer Centricity” means that the company not only aligns processes to customers in order to satisfy customers, e.g. through service within the framework of an existing business model and an existing product range. Rather, “customer centricity” as a concept assumes that both the product range and the business model are called into question and changed when customer needs require it.
The logical basis for “Customer Centricity” lies in the significantly expanded information and communication options for customers and companies on the Internet, which lead to significantly increased transparency. Amazon can be used as a reference company. Amazon has formulated a mission statement that it wants to be the most customer-centric company in the world, and it is implementing this mission. “Customer centricity” can best be measured with the help of the customer lifetime value, which includes both customer loyalty and the customer’s assessment of the company’s problem-solving skills.
- success factor “customer centricity”
- Prerequisite: transparency in customer needs and customer reactions
- Reference company: Amazon
- Central key figure: Customer Lifetime Value
Success factor: Digital innovations
As a model for digital transformation, the E-Commerce Code takes into account that successful companies in the digital economy use digital technologies to develop improved and expanded solutions for customer problems. Increasing efficiency in many processes, especially sales through the use of digital innovations, also leads to increased customer satisfaction, since more products can be delivered faster and cheaper and customers can be reached better. These aspects are captured by the success factor “digital innovations”.
“Digital innovations” implement technological developments in the areas of hardware and software as well as data processing and process control. “Digital innovations” are primarily used to increase the quality of the solution to customer problems or to reduce the cost of problem-solving. In order to act as a central success factor, “digital innovations” must lead to a unique position and lead to competitive advantages. The essential basis for successful innovations lies in the availability of qualified and technologically and entrepreneurially oriented employees, who are known as “smart creatives”.
- Success factor “digital innovations”
- Prerequisite: access to technology and smart creatives
- Reference company: Google
- Indicator: Number of patents & innovations
Success factor: Economies of scale
The third of the strategic e-commerce success factors concerns the growth of product offerings and business models that have been changed with the help of digital innovations. Since these are digital, ie. are based on an interaction of hardware and software, they can at least be reproduced and expanded in the software component at significantly lower costs.
If the product or essential resources in core business processes are also digital – such as digital music or the online shop in e-commerce – the average costs continue to decrease. This leads to above-average profits, which in turn can be invested in further innovations. Economies of scale – in German economies of scale – are the consequence, so that the company has growth rates that are well above average and above all a growth rate that is well above average.
- Success factor “economies of scale”
- Prerequisite: Success factor digital innovations
- Reference company: Uber
- Indicator: the platform’s growth rate
Success factor: Data-Driven marketing
With the growth, the number of available user data and customer contacts increases significantly. Companies can evaluate this data primarily in order to better assess customer reactions to marketing measures. Consequently, “data-driven marketing” is the fourth key success factor for e-commerce. “Data-driven marketing benefits from customer-centricity, because the resulting customer loyalty leads to an increase in usable customer data, the analysis of which can, in turn, be used to increase customer loyalty.
- Data-Driven Marketing as a success factor
- Prerequisite: digital processes and user data
- Reference company: Facebook
- Indicator: number of data analysts in the company
The operationalization of e-commerce success factors
The four success factors of the “The E-Commerce Code” model represent abstract focal points in corporate management that must be operationalized and their success measured. The following therefore provides an overview of which measures are suitable for the operationalization of e-commerce success factors.
Customer Centricity
Customer centricity goes far beyond the usual level of customer orientation in retail. With customer orientation, customers are offered services in an existing business model; with customer orientation, the business model and the product range are continuously adapted to customer preferences.
So how do you know that a company is customer-centric? The most important prerequisite for customer-centricity is the recording of customer preferences. This can be achieved through the following measures:
- Promotion of customer reviews
- Error and quality management
- Comprehensive customer service offering
- Product recommendations as an integral part of customer communication
- The company can be easily reached via several channels
- Active social media marketing with many customer interactions
- Good qualifications of the customer service staff
- For important purchasing parameters, customers have options e.g. Shipping, payment, shipping time
- Use of customer loyalty measures
- Good handling of returns and complaints
- Conversion optimization
- Customer Lifetime Value as a key figure
KPI:
- Customer lifetime value
- Customer Equity
- Retention rate
- Churn rate
- Return rate
- Complaint rate
- Delivery time
- Out-of-stock rate
- Conversion rate
- Newsletter subscribers (net)
Digital Innovations
Digital innovations are likely to be a major challenge for many retailers, as they have so far not seen themselves primarily as technology companies. There can be potential for innovation in both the front end and the back end. Innovations can, therefore, take place in the service area, in customer communication and in the supply chain. Factors for the implementation of the innovations are:
- Own R&D department
- Obtaining patents
- Investing in R&D
- high investment and retention rate
- Number of employees in R&D
- M&A activities in R&D: acquisition and integration of young companies
- Product innovations
- Process innovations
- Dynamic offer structure
- Make instead of buy
KPI:
- Return on Product Development Expense
- Number of patents
- Duration of the patents
- Number of new products per time unit e.g. Months
- Feedback on new products in social media
- Share of sales of new products
Economies of scale
Economies of scale are a consequence of successful digital innovations that can be multiplied at low marginal costs. They require a high degree of focus and a growth strategy. Factors for achieving economies of scale are:
- Growth strategy
- Focus on scaling
- Adequate funding
- Powerful and sustainable online marketing channels
- Network effects are ideal
- General usability of the products and services (“Tooth Brush Test”)
- Internationalization
- Microscale – process steps in the online shop become more effective (e.g. higher shopping cart values)
- Macro scaling – increasing the reach of the online shop
- Control of economies of scale – Define – Measure – Analyze – Improve – Control
- Higher profits per customer visit
- Scaling in logistics: scope of storage, time to market
KPI:
- Output-cost elasticity <1
- User growth rate
- Amount and evolution of the shopping cart
- Conversion rate
- CPO
- CPC
- Shipping costs per order
- Packaging costs per order
- Inventory turnover
- …
Data-Driven Marketing
Data-Driven Marketing is the fourth strategic success factor of the “E-Commerce Code” model. Data-Driven Marketing implements the data that is generated in digital process, supply and communication chains in order to further improve the customer experience. Aspects of the implementation of data-driven marketing are
- Multichannel offers
- Testing
- Responsive website
- Business intelligence
- Data-driven organization
- Personal data analyst etc.
- Data warehouse instead of data silos
- Integrated data processing
E-commerce success factors: conclusion
With this outline, the essential parameters of the four key success factors are outlined. Further research will show how successful e-commerce companies use and implement these factors.
Literature:
- Dominik Große Holtforth (2016): Schlüsselfaktoren im E-Commerce, Berlin, Heidelberg
- Gerrit Heinemann (2010): Der neue Online Handel – Erfolgsfaktoren und Best Practices, 3. Auflage, Wiesbaden
- Mark Jeffery (2010): Data-Driven Marketing – the 15 Metrics Everyone in Marketing Should Know, Hoboken/NJ
Author and Photo/Graphic of this post: Dr. Dominik Große Holtforth